Google E-A-T: The Ultimate Guide To E-A-T SEO
15 Jun 2020|10 MIN READ
Ever since Google’s August 2018 ‘Medic’ algorithm update there has been a lot of discussion around E-A-T SEO and the role it plays in Google’s algorithms.
What is Google E-A-T SEO?
Google E-A-T stands for Expertise, Authoritativeness and Trustworthiness, and is a set of official recommendations for delivering a quality experience online. It focuses on the quality of the content and the creators of that content, as well as the website itself.
Basically, Google wants to ensure that when you search for something, not only do you get the right search results that best match the intent of your query, but that you also get high quality results, with content created by people who demonstrably know what they’re talking about, on websites that you can trust.
At the end of 2022, Google updated its Quality Rater Guidelines to include an additional E (Experience) to better assess search results. What is Google E-E-A-T? Find out in this ultimate guide.
So, how does Google E-A-T measure the Expertise, Authoritativeness and Trustworthiness of your website?
Well, firstly it breaks the analysis down into three dimensions, to analyse:
- The quality of your website
- The quality of the main content on any page
- And the quality of the author(s) of the main content.
This is outlined in detail below.
Why is Google E-A-T SEO so important?
Basically, if Google decides that the quality of your website, the content on it and the creators of that content are not of a sufficiently high standard, then you are unlikely to perform well organically.
Even if, for example, the creators of your content are sufficiently expert in the subject that they are writing about and are regarded as trustworthy authorities.
If this is not made clear to Google, then you’re going to get a low content creator E-A-T score.
Garry Illyes from Google went so far as to say:
“Multiple ‘Baby algorithms’ work together to conceptualise E-A-T metrics.”
Given this, it’s clear that Google E-A-T is core to the way that Google looks at your website and if you ignore E-A-T, and choose to focus on content and technical SEO alone, then you’re missing a vital piece of the algorithmic jigsaw.
It is increasingly important that you send the right signals to Google.
Any SEO audit now needs to include analysis of Google E-A-T recommendations.
How is Google E-A-T SEO measured?
It’s no longer enough to simply create content that matches the intent of your searchers, and optimise it so that it positions well organically. You need to be providing a 360 degree quality experience.
Since Google rolled out its Panda update in February 2011, the message about quality has been clear: if you produce high-quality content you’re going to rank higher than sites that produce low-quality content.
Our understanding of exactly what is meant by ‘High quality content’ became clearer in 2014 when Google first published its E-A-T (Quality Rater) guidelines (more on these below).
According to Danny Sullivan:
“Assessing your own content in terms of E-A-T criteria may help align it conceptually with the different signals that our automated systems use to rank content.”
The guidelines provide examples of the criteria that Google is looking for in terms of signals to satisfy (and presumably score) websites, main content and the author(s) of said main content.
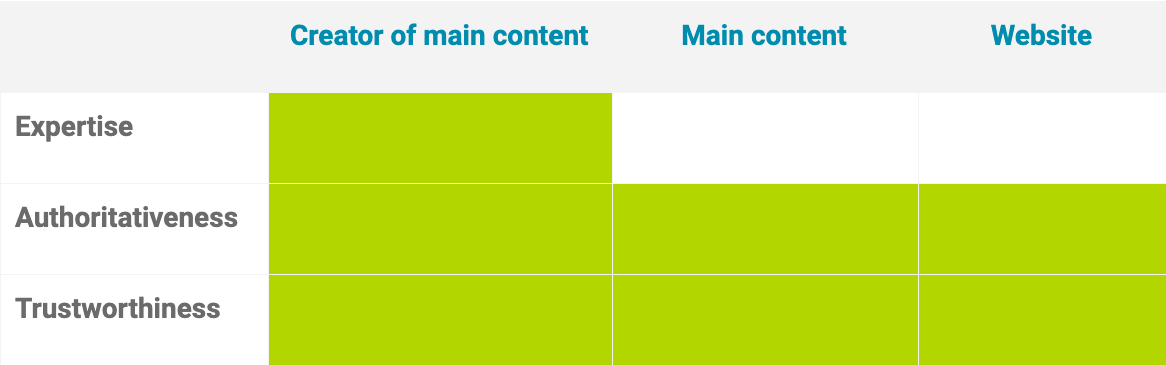
When we boil this down, Google is trying to evaluate the:
- Expertise of the creator(s) of the main content (including headers)
- The authoritativeness of the creator(s), the main content itself and also the website.
- The trustworthiness of the creator(s), the main content itself and also the website
How quality authors satisfy Google E-A-T SEO
When it comes to the expertise of the author of the main content, depending on how much of an impact the subject matter might potentially have on your future health, happiness, financial stability or your safety (see more about these kinds of YMYL sites below), Google will want to see relevant credentials that demonstrate a sufficient level of expertise.
Some websites such as healthline.com demonstrate such expertise really clearly.

Authors who engage with relevant influencers and have an active social media presence, as well as a history of writing for other websites, will naturally be seen as more authoritative than those who don’t.
Author trustworthiness may be determined by what other websites say about this person, as well as the sentiment and responses to post comments.
How quality main content satisfies Google E-A-T SEO
Google’s ‘baby algorithms’ will be applying the same level of scrutiny towards authoritativeness and trustworthiness to the content itself as well as the website.
When it comes to the content itself – Google says that it wants to see a ‘satisfying amount’ of main content. According to the Quality Raters Guidelines, the amount of content necessary for the page to be satisfying depends on the topic and purpose of the page.
Content headers (referred to as titles in the guidelines) need to be descriptive, accurate and helpful. Content with an exaggerated or shocking header will be deemed to be low quality. While ads themselves are fine, distracting ads will result in a low quality rating. User generated content with a lack of curation or oversight may also result in a low quality rating.
How a quality website satisfies Google E-A-T SEO
To determine the authoritativeness and trustworthiness of a website, Google will look for signals off site as well as on. High quality websites are expected to have positive reviews and be recommended by expertise. They might also appear in reviews and articles on sites such as trustradius, financesonline, capterra and glassdoor. Google is easily capable of building up a picture of overall sentiment from sites such as these. One or two isolated negative reviews amongst a majority of glowing reviews will likely be ignored.
Links from other authoritative sites of course are still a key signal of authority.
Where can I see the E-A-T guidelines?
(Search Quality Evaluator)
You can find them here – https://guidelines.raterhub.com/searchqualityevaluatorguidelines.pdf
How does Google E-A-T SEO work?
AI & machine learning fuels E-A-T
According to Google there’s very little technology that the search giant has developed that isn’t using AI and machine learning. (reference: https://www.thinkwithgoogle.com/marketing-resources/ai-personalized-marketing/). Machine learning sits at the heart of AI and attempts to bring meaning to data. Given that the volume of data that Google collects has long surpassed the ability of humans to interpret it and rewrite its algorithms, it would make sense to turn to automated systems that can learn from the data. Not only does machine learning sit at the core of much of what Google does but it is likely to be utilising the inputs (from the quality Raters) to further shape the ‘baby algorithms that in Google’s words, conceptualise E-A-T.
PageRank & Links feed into Google E-A-T
Internal linking is still important to Google as a measure of authority and, despite it not being the hot topic it once was (when support for the PR Toolbar ended in 2016), PageRank is still important as well. As recently as January 2020 Gary Illyes reminded us that PageRank is still a part of their algorithm, while in 2017 he tweeted:
‘DYK that after 18 years we’re still using PageRank (and 100s of other signals) in ranking?
Wanna know how it works?
https://infolab.stanford.edu/~backrub/google.html
DYK that after 18 years we’re still using PageRank (and 100s of other signals) in ranking?
Wanna know how it works?https://t.co/CfOlxGauGFpic.twitter.com/3YJeNbXLml
— Gary 鯨理/경리 Illyes (@methode) February 9, 2017
Given that PageRank works at page level rather than domain level (so let’s stop talking about domain authority alone) and links are an indicator of authority, then what we do with that authority within our internal link architecture becomes increasingly important.
Search ‘Quality raters’ feed into E-A-T
Google employs around 10,000 people as so-called ‘Quality raters’ worldwide.
These raters commonly work on a number of different rating projects using the above guidelines document.
Raters are set tasks of rating websites and individual pages based on E-A-T.
When it comes to rating E-A-T, they are encouraged to look for signals or evidence on-site as well as off.
Quality Raters use ‘Google search operators’ to contribute to E-A-T
The quality rater guidelines demonstrate the use of ‘Google search operators’.
‘Google search operators’ are a specific way of searching to expand the capabilities of regular text searches.
To use ‘Google search operators’, you need to insert a sequence of special characters into Google’s search bar, depending on what you want to find.
This is a task primarily conducted during content research or technical SEO audits.
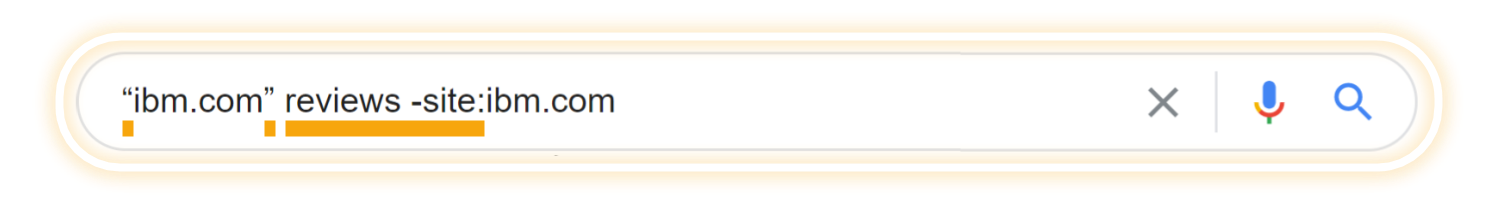
The example above illustrates a search for reviews of “ibm.com”, that excludes pages from ibm.com.
According to Google:
“Ratings will be used to evaluate search engine quality around the world. Good search engines give results that are helpful for people in their specific language and locale.”
According to Danny Sullivan:
“Rater data is not used directly in our ranking algorithms, rather we use them as a restaurant might get feedback cards from diners. The feedback helps us know if our systems seem to be working.”
With that analogy in mind, if restaurant feedback consistently suggested that a meal was too salty, this would most likely lead to a recipe change.
So, is E-A-T a ranking factor?
In the same way that poor food reviews would influence a restaurant to change its recipes, it is highly likely that Google uses rater feedback and other input data to shape relevant algorithms. See more about the effect of E-A-T on ‘Google Core updates’ below.
Quality rater data is teaching the algorithm to understand webpages qualitatively. This understanding will only develop as the algorithm continues to learn autonomously, until one day it is able to decipher content as a human searcher would.
As SEOs, we therefore need to go beyond ticking ‘SEO Ranking Factor’ boxes and offer a 360 degree quality experience that elicits positive sentiment and customer satisfaction across every part of our digital ecosystem.
How are YMYL sites affected by E-A-T SEO?
If a topic or content could potentially impact a person’s future happiness, health, financial stability, or safety then it becomes known as a “Your Money or Your Life” page, or YMYL.
Google has very high ‘Page quality’ rating standards for YMYL pages, because low quality YMYL pages could potentially negatively impact a person’s happiness, health, financial stability, or safety.
The higher the YMYL level, the higher the level of scrutiny.
The Visibility Index chart from Pi’s SEO Platform below illustrates three major credit finance companies (high YMYL) that were negatively impacted by Google’s most recent Core algorithm update that rolled out on May 4th 2020.
Further analysis of one of the websites (CreditKarma) reveals a raft of negative reviews and a very poor (spammy) backlink profile. The chart below shows the acquisition of 22k links in one day, with over 10k links coming from a website that provides dubious login information. From an Authority perspective this is a real negative.
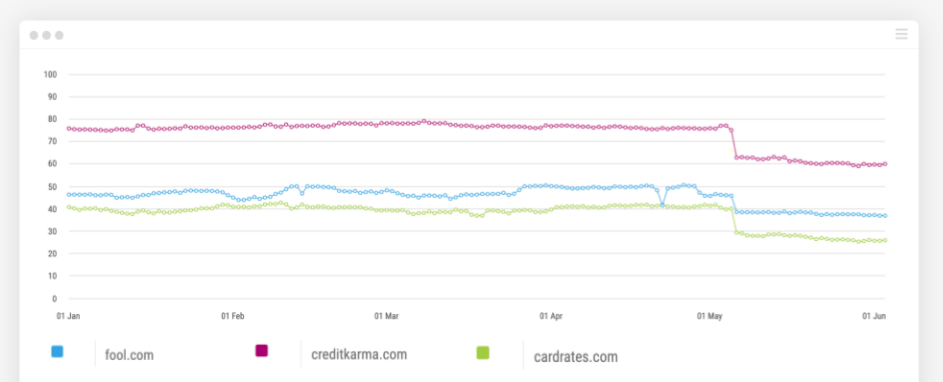
Image source: Pi’s SEO Platform
In addition to these negative authority links, when it comes to Trust, the third dimension of E-A-T, it would seem there are further negative signals from authoritative websites that Google will be able to quickly discover:
This satisfaction rating comes from the Consumer Affairs website (https://www.consumeraffairs.com/online/credit-karma.html)

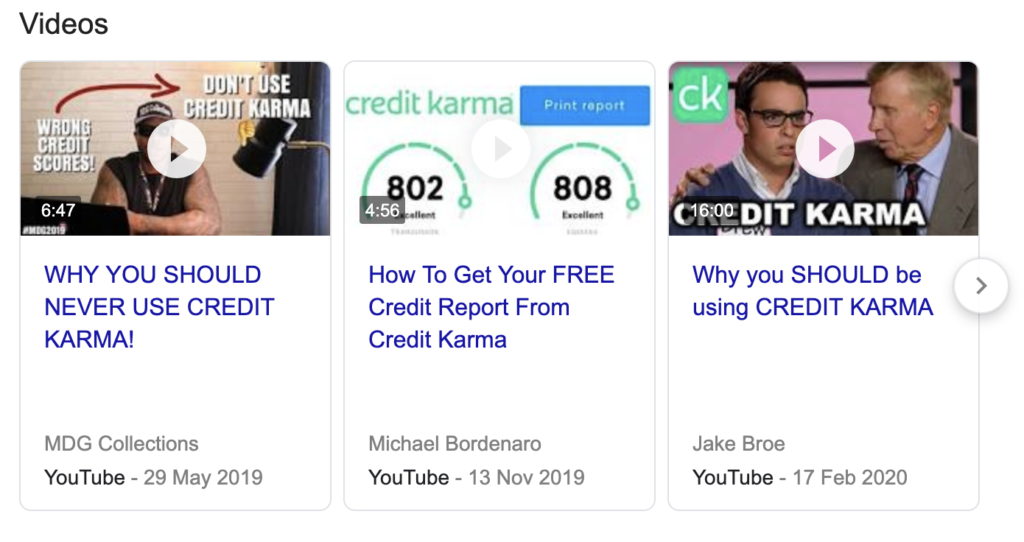
Further mixed reviews are quickly surfaced on Youtube:
Quality Raters are explicitly told to:
‘Look for reviews, references, recommendations by experts, news articles, and other credible information created/written by individuals about the website’.
So you can be pretty sure that Google will be doing exactly this.
The Quality Raters guidelines adds:
‘Recommendations from expert sources, such as professional societies, are strong evidence of very positive reputation.’
‘Be skeptical of both positive and negative user reviews’
However, if negative reviews substantially outweigh the positive then Google will have no trouble in understanding this.
So it’s really important to monitor what others are saying about your brand, your website and the service and products you offer.
Where do Google’s Core Algorithm updates fit into E-A-T?
Referring back to Garry Illyes’ quote about Google E-A-T and baby algorithms, it is fairly safe to assume that when those algorithmic levers are turned based on hundreds of signals – including Quality Rater data – the bigger the shake up we see in the days after Core updates.
Notice the three websites above show no sign of immediate bounceback? Even if you identify the gaps and put them right, it is evident that as far as Google is concerned, Authoritativeness and Trust are hard earned. And rightly so.
According to Danny Sullivan:
“Broad core updates tend to happen every few months. Content that was impacted by one might not recover – assuming improvements have been made – until the next broad core update is released.”
Track your daily SERP performance
Has the SERP landscape changed since the May update?
Analysing one sector related to employee performance management we can see a pattern across a number of search terms where there do appear to be more features within the SERP landscape.
Here is an example Matrix view for the query: ‘Approaches to performance management and appraisal’ in the period before the update:
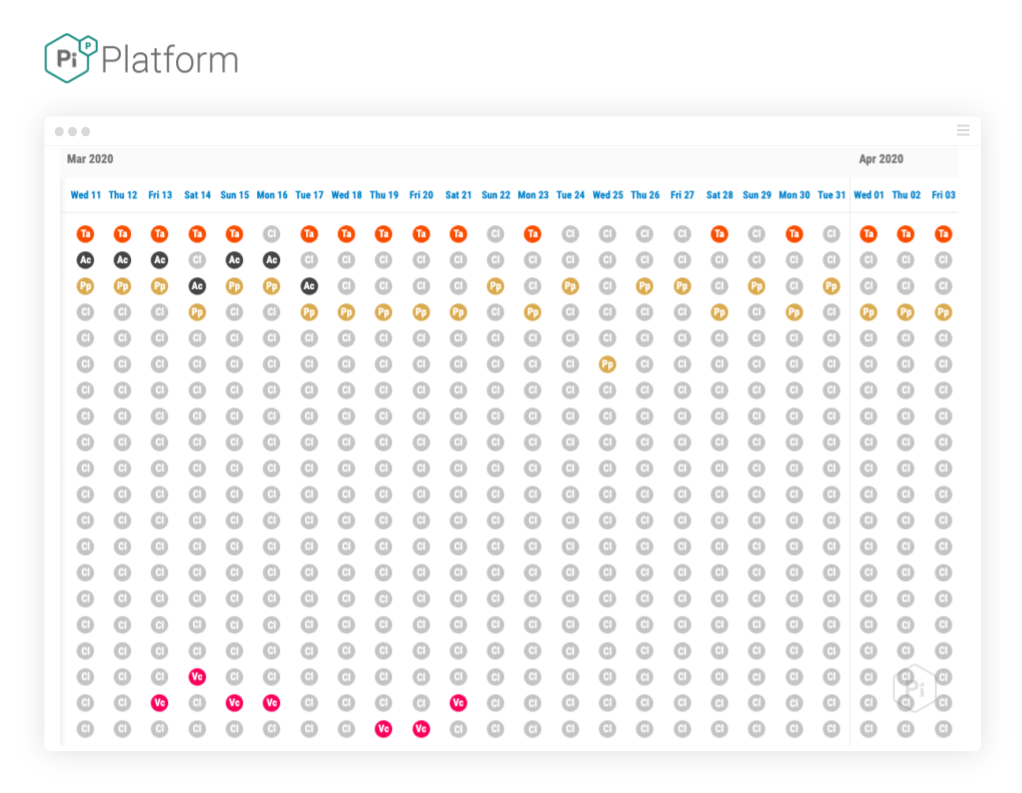 Image source: Pi’s SEO Platform
Image source: Pi’s SEO Platform
And here for the period after the May 04 update, post settle down period:
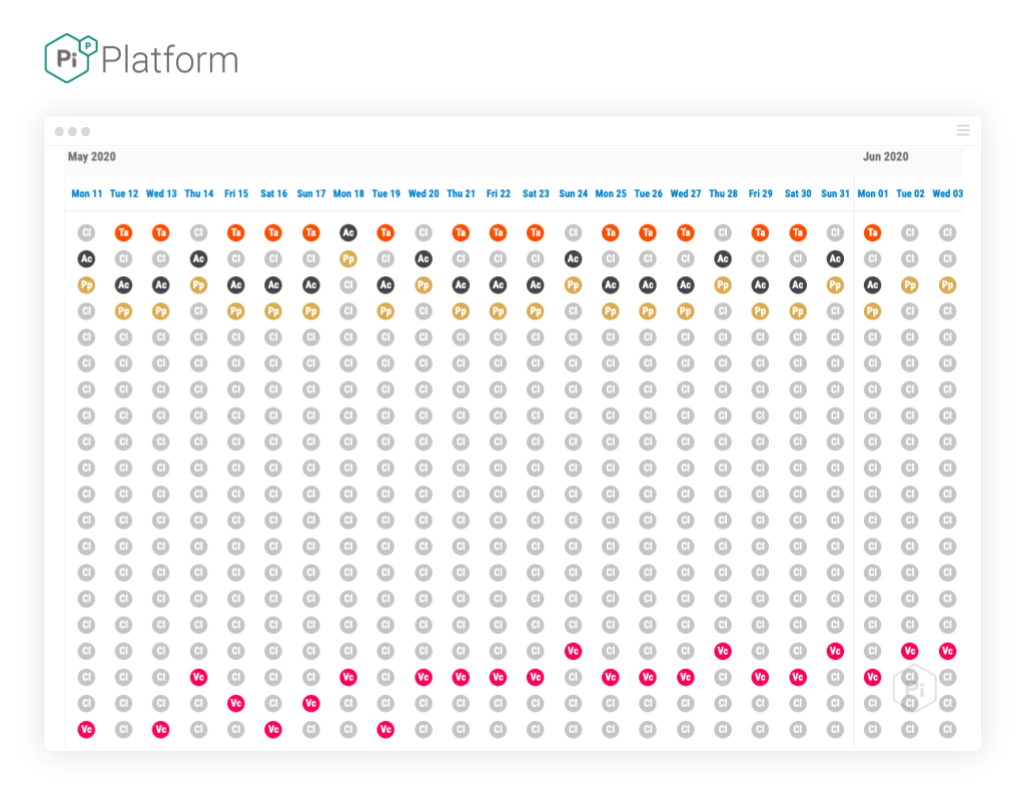 Image source: Pi’s SEO Platform
Image source: Pi’s SEO Platform
- Video Carousel up 288%
- Answer Cards up 214%
This is for Desktop searches. In mobile the SERP was equally feature rich.
Within this sector there was a stand-out winner from the May 04 algo update seen in the Visibility Index below:
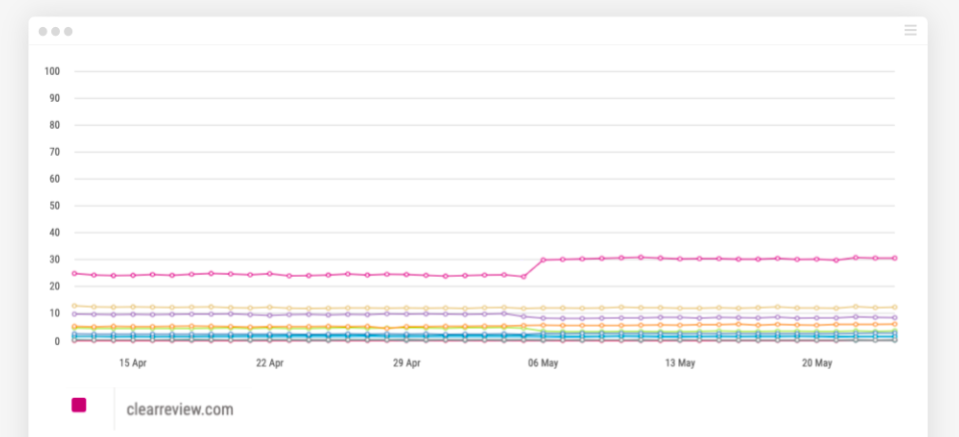
The only site out of these 11 to see a noticeable uplift was Clearreview.com.
This Index is based upon performance for over 800 search terms in Google UK.
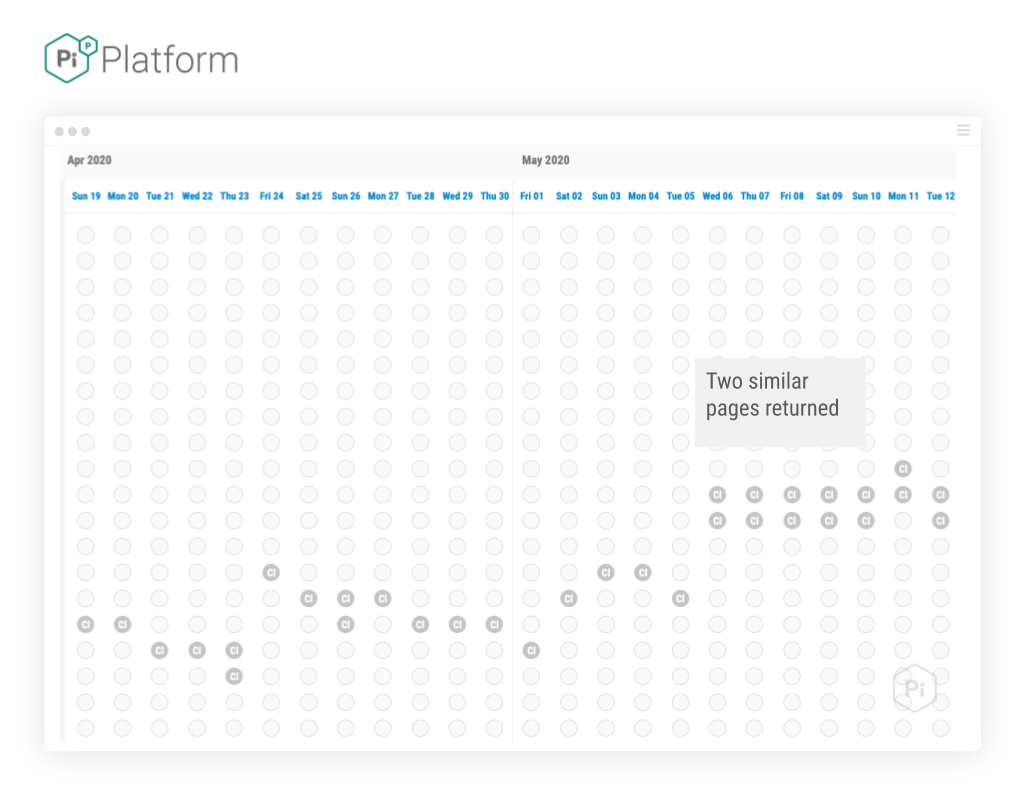
Using the same search term shown in the Matrix views above, we can see that Clearreview.com shows signs of a significant visibility update. Firstly, performance for the same query – in the same period pre update:
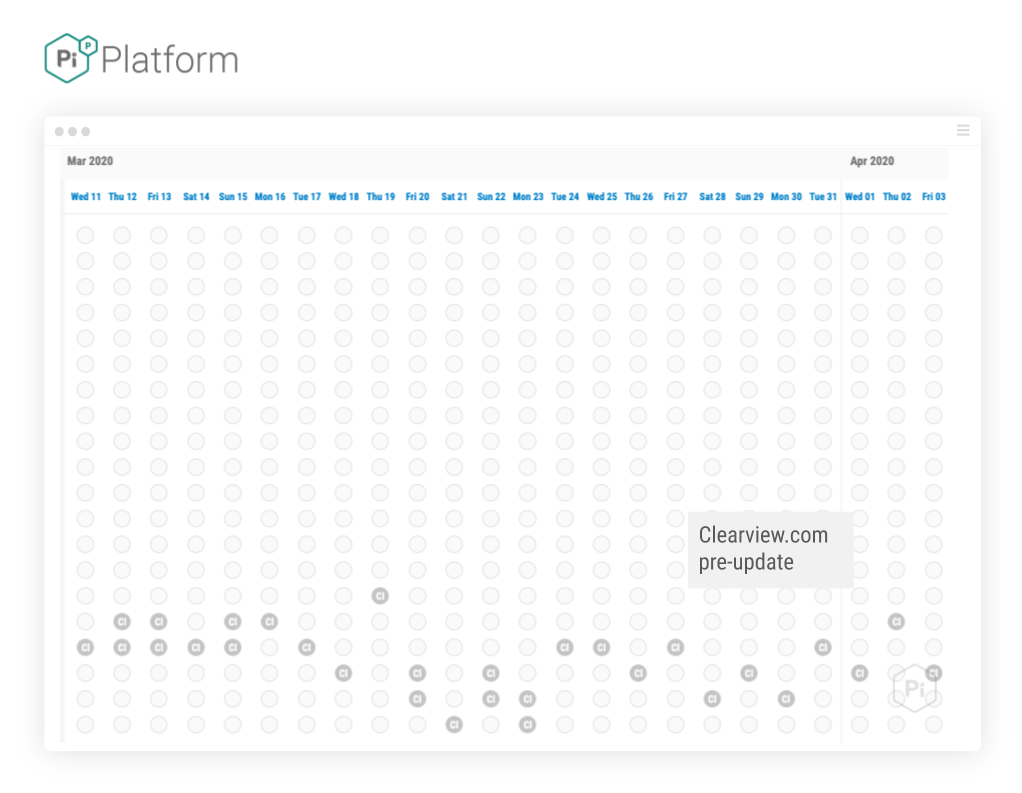
And here is their visibility in the same period, after the update:
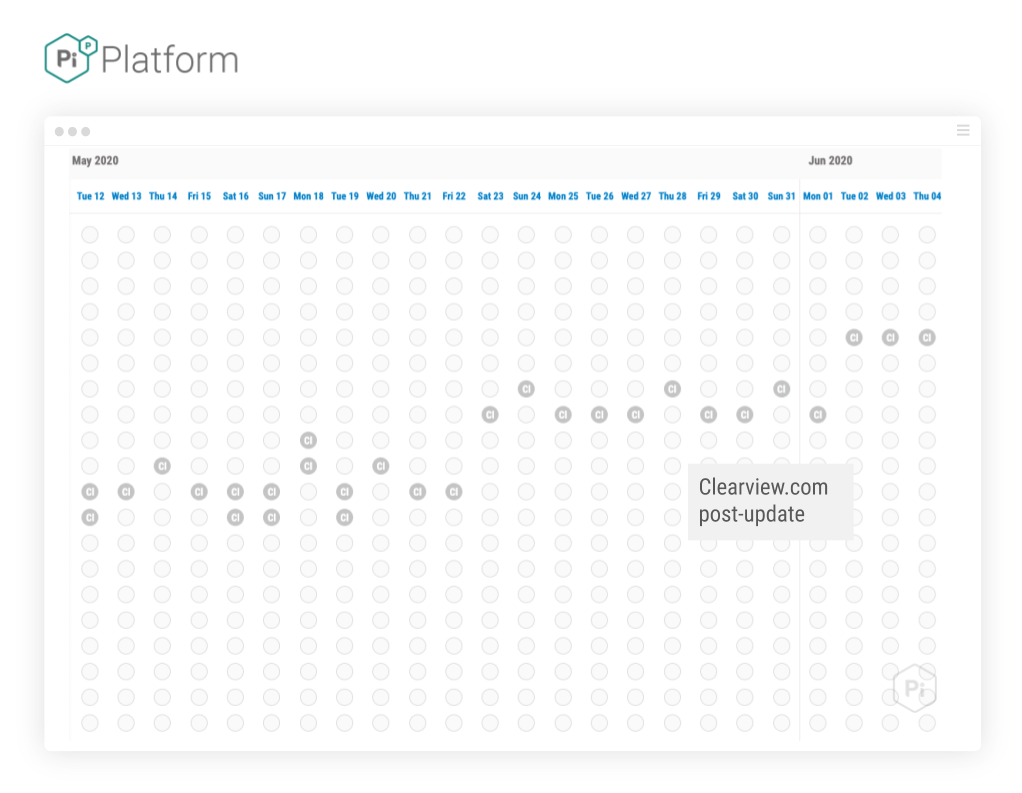
Interestingly, immediately after the update, Google started clustering two similar pages, high in the SERP where previously only one, in the main was returned:
This should be remembered when thinking about targeting Google’s Answer Card as a semantically related piece of content will potentially act as a substitute classic link when the page from which the answer card is drawn vanishes.
Explore algorithm updates in Pi Platform
Evidence of high E-A-T
Lets begin with the obvious off-site signals that Google’s Quality Raters are shown to use. Here we’re looking to see what people are saying about cleareview.com and by the looks of it they’re saying incredibly positive things:
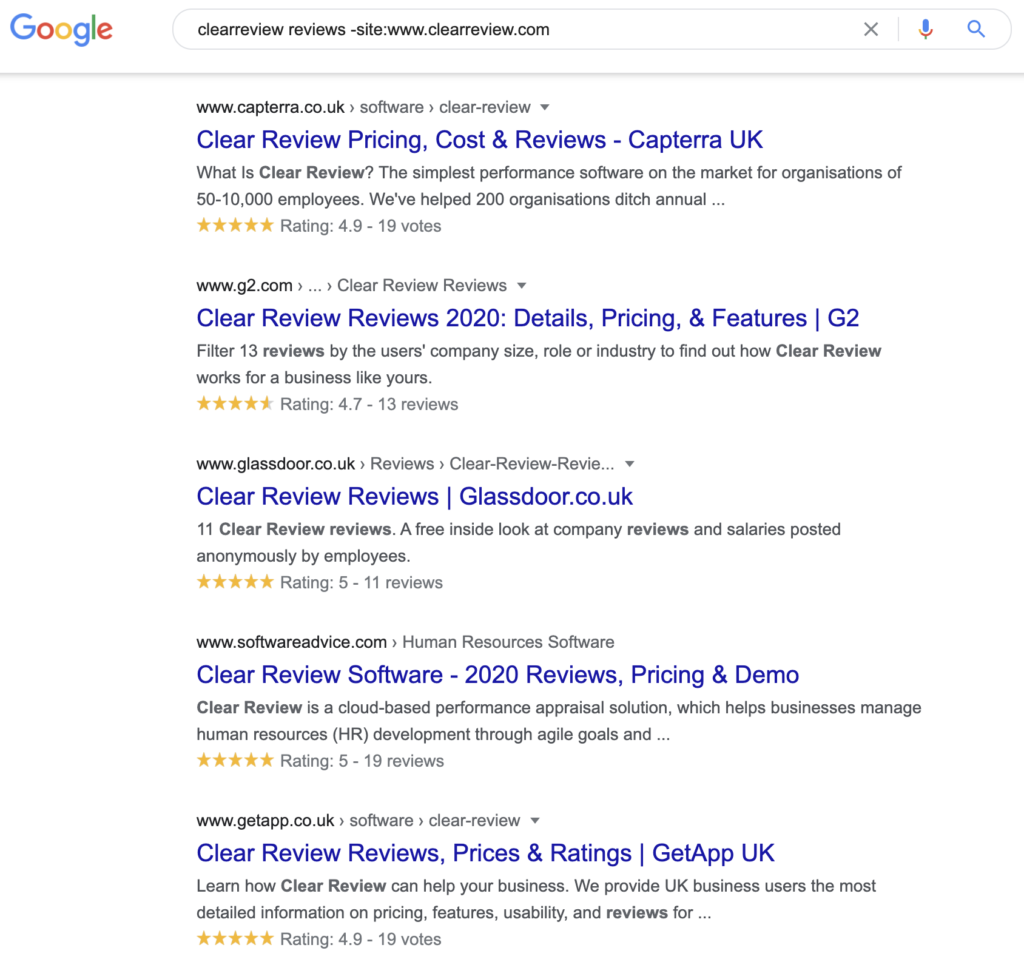
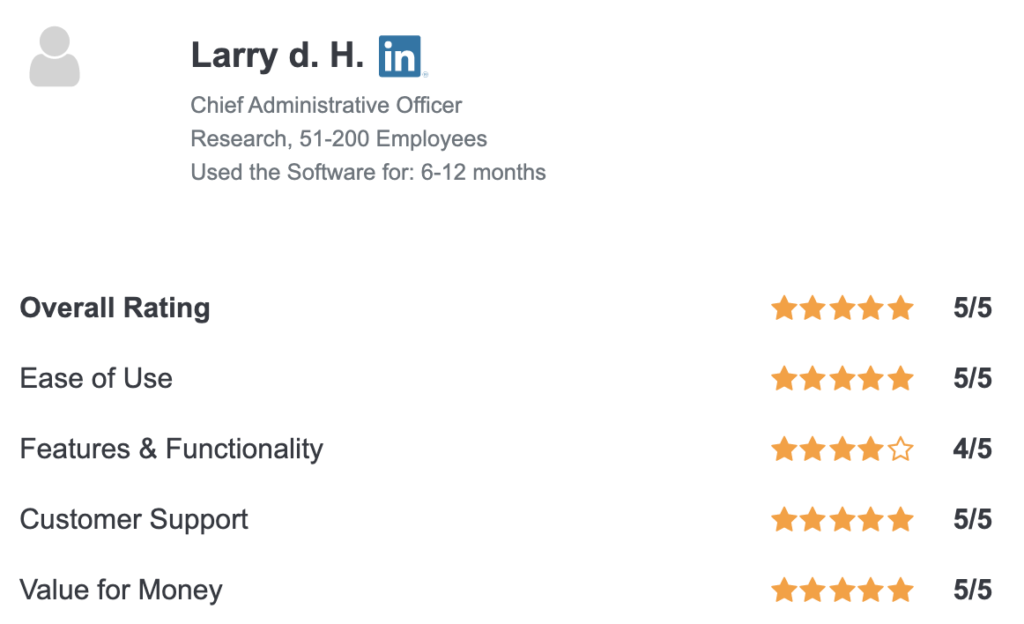
Here’s that first review on Capterra.co.uk
And here’s some evidence of E-A-T on the clearreview.com website itself in a recent blog post:

The above paragraph references an Authoritative source – McKinsey and also links to footnotes with further Expert and Authoritative signals.

Do I trust this content? It’s got to be a yes!
Building on your E-A-T
The insight in the Matrix is clear. This page has moved from Page two of Google to a consistent page one position. There is an answer card in place but the quality of it is not great and it is from a US domain. Additionally it’s not stable with three domains switching the Answer Card four times in the past 24 days. Google’s not convinced enough that one of these is the right one and with this level of flux, might welcome a fresh answer to these questions from a high Google E-A-T website:

There will be many websites that are now in a position to benefit from this latest Core algorithm update. It’s not enough to sit back and take any uplift that you’re given by the update, as good as that is; this is the time to act and leverage your E-A-T by utilising the data and the insights within it to make the most of opportunities such as this one.
What can I do to improve my Google E-A-T SEO score?
Create a quality website:
- Include reviews
- Make company information clear & easy to find
- Company history
- Date founded
- Team bios
- Author bios
- Contact us
- Customer service
- Reviews / Ratings
- Returns
- Get recommended by experts in your field
Quality raters (see below) look into what others say about your site. Does this mean that as well as doing both a technical and content audit we need to begin doing reputation audits on both our website and its authors? The answer is YES – especially for YMYL sites (see more below). - Include references throughout your site
- News articles
- Other credible information written about the website
Deliver quality main content:
- Create a satisfying amount of high quality main content
- Include a descriptive or helpful title (H1)
Avoid shocking, exaggerated or click-bait headlines - Build a positive reputation
- Ensure there are no errors (i.e. grammatical, factual etc.)
- Offer clear website information
Become a quality author:
- Be active on social media
Be sure to share useful and unique information - Engage with other influencers
- Write guest posts on other sites
- Feature in a range of content formats
- Articles
- Webinars
- Podcasts etc.
- Feature in a range of content formats
- Create a personal / company website
- Ensure you are referenced on a range of sites
- Create an author bio page on your website
- Photo
- Full name
- A description of your areas of expertise
- Links to other publications / websites you’ve written for including your personal website
- Social profiles Encourage other sites you create content for to do the same
- Use schema to tell Google who you are
- Claim the Google Knowledge Panel for your name
- Add alt text to your image headshots
Not only will you lose customers and ranking if your content / website is of poor quality, if you don’t provide an appealing experience for authors, guest bloggers, influencers or partners on your website (i.e. if you don’t make space for author bios on your website) in the future could this affect your ability to get contributions from them.
And lastly…
- Read the Quality Raters Guidelines and search within it for your sector
- Try to emulate the highest quality examples
- Include author names and bios
- Monitor and build credibility on 3rd party websites
- Make sure ads aren’t intrusive
- Link to credible sources
- Make it clear who you are and try to demonstrate your expertise
- Use Schema to help search engines join up the dots
- Utilise internal links carefully to channel authority
- Monitor your organic performance. It’s critical to understand if you’ve been impacted and to what extent
In December 2022, Google added an extra ‘E’ which signifies Experience, entering Google E-E-A-T, read our latest blog post on it.
Demo the software today
Never miss a post
Join our mailing list and have our SEO news delivered straight to your inbox.





